Sudan located in northeastern Africa, is a vast and diverse country with a rich cultural heritage and a diverse landscape. Spanning a significant portion of the African continent, Sudan is bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, and Libya to the northwest
Sudan’s Geographical Coordinates
Sudan is situated between latitudes 8° and 23°N and longitudes 22° and 38°E. These coordinates place Sudan in the northeastern part of Africa, bordering both the Red Sea and the Sahara Desert.
Boundaries and Bordering Countries
Sudan shares borders with several countries. To the north, it is bordered by Egypt, while Eritrea and Ethiopia lie to the east. South Sudan is located to the south, and the Central African Republic is to the southwest. Chad is situated to the west, and Libya forms Sudan’s northwest border.
Sudan’s Regional Divisions
Sudan is divided into 18 states, which are further divided into localities. These states include Khartoum, Red Sea, White Nile, Blue Nile, Northern State, and others. Each state has its unique geographical characteristics, contributing to the country’s diversity.
The Nile River: Lifeline of Sudan
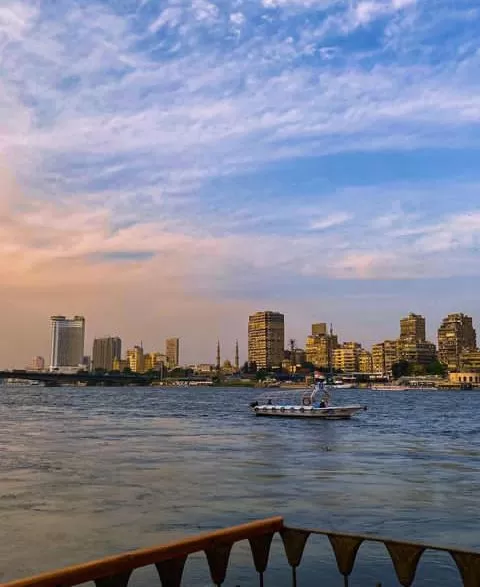

The Nile River, the world’s longest river, runs through Sudan, shaping its landscape and providing a vital water source. The Nile divides Sudan into eastern and western regions, with its tributaries nourishing the surrounding areas. This mighty river is not only crucial for agriculture and transportation but also offers picturesque views and opportunities for tourism.
Darfur: A Region of Natural Beauty

Located in western Sudan, the region of Darfur is known for its stunning natural landscapes. From the rugged Jebel Marra volcanic massif to vast savannahs and rocky escarpments, Darfur showcases the diverse beauty of Sudan’s terrain.
Red Sea Coastline and Ports
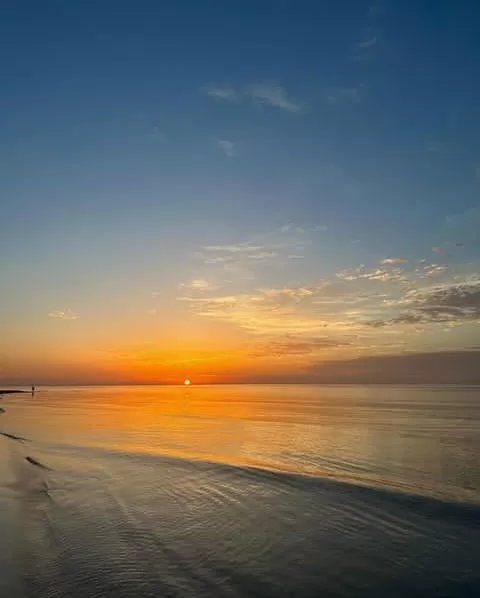

Sudan’s eastern border is defined by the Red Sea coastline, stretching for approximately 750 kilometers. This coastal region is home to vibrant coral reefs, marine life, and pristine beaches. Ports such as Port Sudan play a crucial role in international trade and are gateways for the country’s maritime connections.
Desert Landscapes: Sahara and Nubian Deserts

A significant portion of Sudan is covered by the Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world. The country’s northern regions are dominated by vast expanses of golden sand dunes and arid landscapes.
Sudan’s Climate: From Desert to Tropical
Due to its vast size and geographical diversity, Sudan experiences a range of climates. In the northern regions, where the Sahara Desert prevails, the climate is arid and extremely hot, with minimal rainfall. As we move southward, the climate transitions to a more tropical savannah type, characterized by a wet and dry season. The southern parts of Sudan receive higher amounts of rainfall, supporting lush vegetation and agricultural activities.
Rich Natural Resources
Sudan is blessed with abundant natural resources that contribute to its economic potential. The country is known for its reserves of gold, copper, uranium, iron ore, and other minerals. Additionally, Sudan has vast agricultural lands, making it a significant producer of crops such as sorghum, cotton, and sesame.
Wildlife and Biodiversity
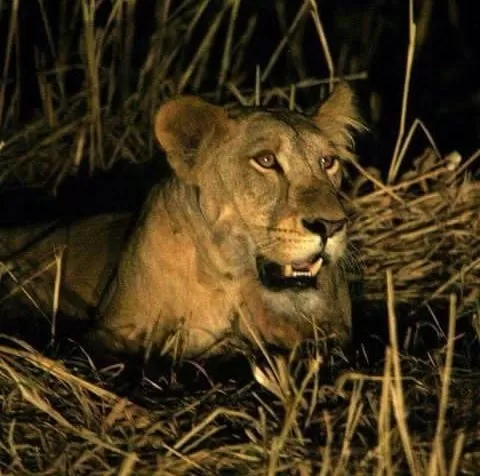

Despite the challenging environmental conditions, Sudan is home to diverse wildlife and biodiversity. National parks and reserves, such as Dinder National Park and Radom National Park, provide habitats for a variety of species.
Sudan’s wildlife includes elephants, giraffes, lions, cheetahs, gazelles, and numerous bird species, making it a destination for nature enthusiasts and safari lovers.
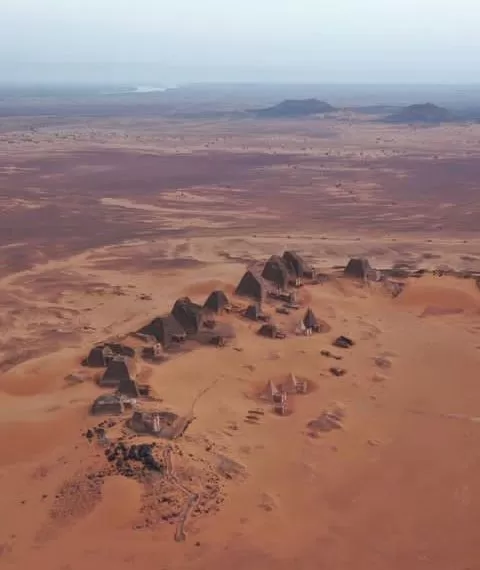
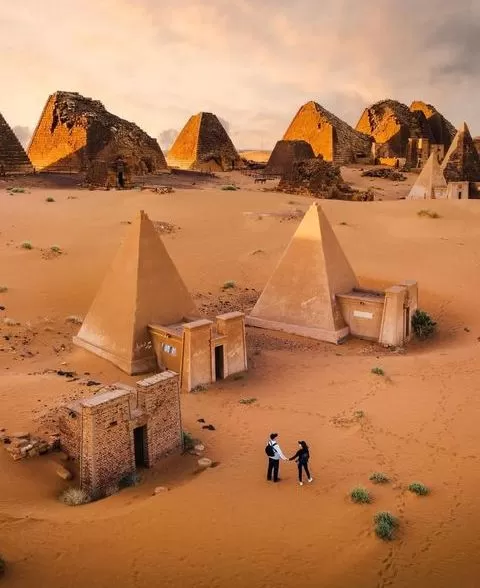
Historical and Cultural Sites
Sudan’s rich history and cultural heritage are reflected in its numerous archaeological sites and ancient civilizations. The country is known for the pyramids of Meroe, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, which date back to the Kingdom of Kush. Other notable sites include the ancient city of Napata, the temples of Naqa and Musawwarat es-Sufra, and the historic city of Dongola.
Economic Importance and Development
Sudan’s geographical location, with its connections to neighboring countries, plays a crucial role in its economic significance.
It serves as a transit hub for trade routes linking North Africa, East Africa, and the Middle East. Additionally, Sudan’s natural resources, agriculture, and potential for renewable energy contribute to its economic development and investment opportunities.
Sudan’s Strategic Position in Africa
Given its strategic location, Sudan holds geopolitical importance within the African continent. It serves as a bridge between North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa and is an active participant in regional organizations such as the African Union and the Arab League.
Sudan’s role in regional stability and diplomatic relations positions it as a key player in African affairs.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Sudan possesses great potential, it also faces various challenges. These include political instability, economic disparities, water scarcity, and conflicts in certain regions.
However, the country is actively working towards addressing these issues and harnessing its resources for sustainable development, including initiatives for infrastructure improvement and economic diversification.
Sudan’s location in northeastern Africa grants it a unique position with diverse landscapes, cultural heritage, and economic opportunities.
From the vast deserts to the fertile riverbanks, Sudan offers a blend of natural wonders, historical treasures, and vibrant communities. As the country continues to navigate its path towards progress, it remains a place of intrigue and promise.
FAQs
1. Is Sudan safe for travelers?
Sudan has areas that are considered safe for travelers, but it’s essential to research and stay informed about the current situation before planning a trip. Check travel advisories and consult with local authorities or tour operators for the latest information.
2. Can I visit the pyramids of Meroe?
Yes, the pyramids of Meroe are open to visitors. It’s a remarkable archaeological site where you can explore the ancient history and marvel at the well-preserved pyramids.
3. What languages are spoken in Sudan?
The official language of Sudan is Arabic, which is widely spoken throughout the country. However, there are also numerous local languages spoken by different ethnic groups, such as Beja, Fur, Nubian, and Dinka, among others.
4. Are there opportunities for wildlife safaris in Sudan?
Yes, Sudan offers opportunities for wildlife safaris, particularly in its national parks and reserves. These protected areas provide a chance to observe diverse wildlife, including elephants, giraffes, and lions, in their natural habitats.
5. How can I access more information about traveling to Sudan?
For more information about traveling to Sudan, including visa requirements, safety guidelines, and tourist attractions, it is advisable to consult with the Sudanese embassy or consulate in your country. They can provide you with the most up-to-date and accurate information.
Thank you for reading this article.
See also
Tunisia Travel Guide: Discover the Riches of North Africa
Namibia Africa: A Beautiful Destination To Visit
Interesting Facts You Need To Know About Tanzania In Africa
Interesting Facts and Information About Kenya in Africa
